What Is Xylem?
Xylem is a vascular tissue in plants that transport water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant and also provides physical support. Xylem is found in all vascular plants including the seedless club mosses, ferns, horsetails as well as all gymnosperms (flowering plants) and gymnosperms (plants with seeds unenclosed in an ovary). Xylem formation begins when the actively dividing cells of growing root and shoot tips (apical meristems) give rise to primary xylem.
Xylem tissue consists of a variety of specialized water-conducting cells referred to as tracheary elements. The xylem tracheary elements consist of cells known as tracheids and vessel members, both of which are typically narrow, hollow and elongated. Tracheids are less specialized than the vessel members and are the only type of water-conducting cells in most gymnosperms and seedless vascular plants. In addition to the tracheary elements, xylem tissue also features fibre cells for support and parenchyma (thin-walled, unspecialized cells) for the storage of various substances.

Facts About Xylem
- The word Xylem is derived from a Greek word ‘Xylon’ meaning wood.
- Xylem is the complex tissue of plants responsible for transporting water and other nutrients absorbed from the roots to the rest of the plant.
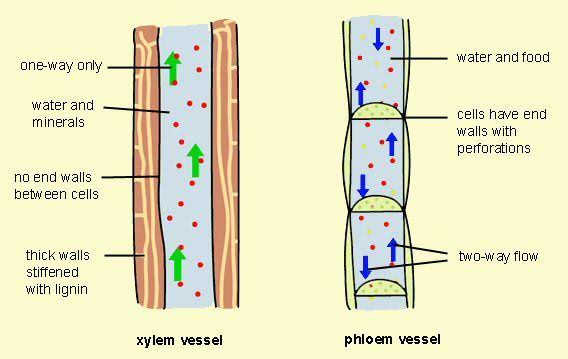
- Xylem tissues are tubular-shaped structure, with the absence of cross walls. This tissue resembles the shape of a star.
- Consists of mainly dead cells (only parenchyma is the living cells in the xylem.
- It consist of tracheids, vessel elements, xylem parenchyma, xylem schlerenchyma and xylem fibres.
- It is located in the center of the vascular bundle.
- The conductive tissue in the xylem is dead (Tracheids and Vessels).
- Amount of xylem is more than that of phloem in the vascular bundle.
- Majority of the cells in the xylem are thick walled cells.
- In mature plants, the xylem forms the majority bulk of the plant body.
- In mature plants, the wood (xylem) is differentiated into heartwood and sapwood.
- Xylem fibres are usually smaller.
- Xylem occupies inner to the vascular cambium.
- Transport through xylem is unidirectional; the water and mineral are only moved up from the roots.
- Tylose formation occurs in the xylem.
- Xylem can provide mechanical support.
- The main function of xylem is conduction of water and minerals.
- Conducting elements (Tracheary elements) have different types of wall thickenings.
- Vessels are devoid of septa.
- The tracheary elements (conducting elements) have lignin thickening in the walls.
Also Read: Difference Between C3 And C4 Plants
What Is Phloem?
Phloem also referred to as bast tissue, is the living tissue in vascular plants that transport soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis referred to as photosynthates, in particular the sugar sucrose from the leaves to all other parts of the plant where they are needed. Transport in the phloem is both up and down the stem. Transport of substances in the phloem is referred to as translocation.
Phloem is composed of various specialized cells i.e:
- Sieve tubes
- Companion cells
- Phloem fibres
- Phloem parenchyma cells
- Sclerenchyma
Sieve tubes are columns of sieve-tube cells having perforated, sieve-like areas in their lateral or end walls, provide the channels in which food substances travel. Phloem fibres are flexible long cells that make up the soft fibres. Phloem Parenchyma cells are located near the finest branches and terminations of sieve tubes in leaf veinlets, where they also function in the transport of foods. Companion cells have a nucleus and packed with dense cytoplasm containing many ribosomes and mitochondria. This means that the companion cells are able to undertake the metabolic reactions and other cellular functions, which the sieve elements cannot perform. The Sclerenchyma is the main support tissue of the phloem, which provides stiffness and strength to the plant.

Facts About Phloem
- The word Phloem a Greek word ‘phloios’ meaning bark.
- Phloem is a vascular tissue that transports soluble organic compounds prepared during photosynthesis from the green parts of the plant to the rest of the plant.
- Phloem tissues are tubular-shaped, elongated structures with the presence of walls within sieve tubes.
- Consists mainly of living cells (only fibres are the dead cells in phloem).
- It consists of four elements: companion cells, sieve tubes, bast fibres, phloem fibres, intermediary cells and the phloem parenchyma.
- It is located on the outer side of the vascular bundle.
- The conducting cells in the phloem (sieve elements) are living.
- Amount of phloem is less than that of xylem in the vascular bundle.
- Majority of the cells in the phloem are thin walled cells.
- In mature plants, the phloem forms the major bulk of the bark.
- There is no differentiation of phloem into heartwood and sapwood.
- Phloem fibres are usually larger and are referred to as bast fibres.
- Phloem occupies outer to the vascular cambium.
- Transport through phloem is bidirectional; the food can move both up and down the plant.
- Tylose formation does not occur in the phloem.
- Phloem cannot provide mechanical support.
- The main function of phloem is conduction of food materials.
- Wall thickenings are absent in the conducting channels.
- Sieve tubes have bulging and porous septa.
- Walls of the sieve tube (conducting element) do not possess lignin.
Similarities Between Xylem And Phloem
- Both xylem and phloem are developed from the cambium.
- Both phloem and xylem show primary and secondary.
- Both xylem and phloem are complex tissue composed of more than one type of cells.
- Both are the components of vascular tissue system of plants.
- Both phloem and xylem contain living and dead cells.
- Both contain parenchymatous cells.
- Both phloem and xylem contain fibres.
- In primary vascular bundles both xylem and phloem are differentiated into proto and Meta elements.
Also Read: Difference Between Gymnosperms And Angiosperms
Difference Between Phloem And Xylem In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | XYLEM | PHLOEM |
| Name Derivation | The word Xylem is derived from a Greek word ‘Xylon’ meaning wood. | The word Phloem a Greek word ‘phloios’ meaning bark. |
| Description | Xylem is the complex tissue of plants responsible for transporting water and other nutrients absorbed from the roots to the rest of the plant. | Phloem is a vascular tissue that transports soluble organic compounds prepared during photosynthesis from the green parts of the plant to the rest of the plant. |
| Structural Shape | Xylem tissues are tubular-shaped structure, with the absence of cross walls. This tissue resembles the shape of a star. | Phloem tissues are tubular-shaped, elongated structures with the presence of walls within sieve tubes. |
| Nature Of Cells | Consists of mainly dead cells (only parenchyma is the living cells in the xylem. | Consists mainly of living cells (only fibres are the dead cells in phloem). |
| Main Components | It consist of tracheids, vessel elements, xylem parenchyma, xylem schlerenchyma and xylem fibres. | It consists of four elements: companion cells, sieve tubes, bast fibres, phloem fibres, intermediary cells and the phloem parenchyma. |
| Location | It is located in the center of the vascular bundle. | It is located on the outer side of the vascular bundle. |
| Conductive Tissue | The conductive tissue in the xylem is dead (Tracheids and Vessels). | The conducting cells in the phloem (sieve elements) are living. |
| Quantity | Amount of xylem is more than that of phloem in the vascular bundle. | Amount of phloem is less than that of xylem in the vascular bundle. |
| Size Of The Walls | Majority of the cells in the xylem are thick walled cells. | Majority of the cells in the phloem are thin walled cells. |
| Mature Plants | In mature plants, the wood (xylem) is differentiated into heartwood and sapwood. | In mature plants, the phloem forms the major bulk of the bark. |
| Differentiation | In mature plants, the wood (xylem) is differentiated into heartwood and sapwood. | There is no differentiation of phloem into heartwood and sapwood. |
| Fibre Size | Xylem fibres are usually smaller. | Phloem fibres are usually larger and are referred to as bast fibres. |
| Position Around Vascular Cambium | Xylem occupies inner to the vascular cambium. | Phloem occupies outer to the vascular cambium. |
| Transport | Transport through xylem is unidirectional; the water and mineral are only moved up from the roots. | Transport through phloem is bidirectional; the food can move both up and down the plant. |
| Tylose Formation | Tylose formation occurs in the xylem. | Tylose formation does not occur in the phloem. |
| Mechanical Support | Xylem can provide mechanical support. | Phloem cannot provide mechanical support. |
| Main Function | The main function of xylem is conduction of water and minerals. | The main function of phloem is conduction of food materials. |
| Wall Thickenings | Conducting elements (Tracheary elements) have different types of wall thickenings. | Wall thickenings are absent in the conducting channels. |
| Septa | Vessels are devoid of septa. | Sieve tubes have bulging and porous septa. |
| Conducting Elements | The tracheary elements (conducting elements) have lignin thickening in the walls. | Walls of the sieve tube (conducting element) do not possess lignin. |
Also Read: Difference Between Evergreen and Deciduous Trees