What Is An Aldose Sugar?
Aldoses are a type of monosaccharide that contains an aldehyde group on its carbon skeleton. Generally, an Aldose contains an aldehyde with two or more hydroxyl groups attached; one of the hydroxyl groups is at the end opposite to the aldehyde. The aldehyde group is a reactive chemical group denoted as (-CH=O). The chemical formula of Aldose is written as Cn(H2O)n.
Examples Of Aldoses
- Glycolaldehyde
- Glyceraldehydes
- Erythrose
- Threose
- Glucose
- Galactose

Characteristic Of Aldose
- Aldose is a type of monosaccharide that contains an aldehyde group group (-CH=O) on its carbon skeleton. Generally, there is one aldehyde group per each monosaccharide molecule.
- Aldose structure has one carbon.
- In Seliwanoff’s test (where the sample is heated with acid and resorcinol), aldoses tend to respond at a moderate pace and deliver a slow light pink color.
- Aldoses may decompose into ketose depending on the isomerization reaction.
- The chemical names of the Aldose sugars depend on the number of carbon atoms they possess.
- Aldoses are primarily found in plants. A good example is glucose.
- Aldose is a pure sugar.
- The chemical formula of Aldoses is written as Cn(H2O)n.
What Is A Ketose Sugar?
Ketose is a type of monosaccharide where the carbon skeleton contains a ketone group. The ketone group is a reactive chemical group denoted as (-C=O). The simplest form of ketose is the sugar molecule made up of three carbon atoms, the middle on with the ketone group. Just like Aldoses, ketoses also have many stereogenic centers within the carbon chain.
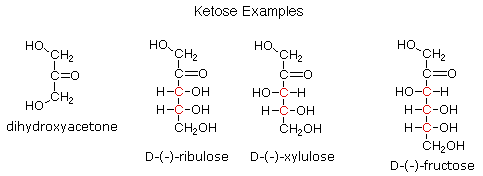
Examples of ketose Sugars
- Fructose
- Ribulose
- Xylulose
- Erythrulose
- Tagatose
- Sorbose
- Pentoses
- Hexoses
- Octoses
- Nanoses
- Tetroses etc.
Characteristics Of Aldose
- Ketose is a type of monosaccharide where the carbon skeleton contains a ketone group (-C=O).
- Ketose structure has three carbon atoms.
- In Seliwanoff’s test, ketoses react with the crystalline compounds whose name is resorcinol to give a deep cheery-red color.
- Ketose can isomerize into Aldose only if the carbonyl group is at the end of the chain.
- The chemical names of the ketose sugars depend on the number of carbon atoms they possess.
- Ketoses can be found in processed foods. A good example is fructose.
- Ketose is an impure sugar.
- The chemical formula of ketose is written as RCOR. Where R is the ketose functional group (-C=O).
Difference Between Aldose And Ketose In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON
|
ALDOSE | KETOSE |
| Description | Aldose is a type of monosaccharide that contains an aldehyde group group (-CH=O) on its carbon skeleton. Generally, there is one aldehyde group per each monosaccharide molecule. | Ketose is a type of monosaccharide where the carbon skeleton contains a ketone group (-C=O). |
| Number Of Carbon Atoms | Aldose structure has one carbon. | Ketose structure has three carbon atoms. |
| Seliwanoff’s Test | In Seliwanoff’s test (where the sample is heated with acid and resorcinol), aldoses tend to respond at a moderate pace and deliver a slow light pink color. | In Seliwanoff’s test, ketoses react with the crystalline compounds whose name is resorcinol to give a deep cheery-red color. |
| Isomerization Reaction | Aldoses may decompose into ketose depending on the isomerization reaction. | Ketose can isomerize into Aldose only if the carbonyl group is at the end of the chain. |
| Chemical Names | The chemical names of the Aldose sugars depend on the number of carbon atoms they possess. | The chemical names of the ketose sugars depend on the number of carbon atoms they possess. |
| Presence | Aldoses are primarily found in plants. A good example is glucose. | Ketoses can be found in processed foods. A good example is fructose. |
| Nature | Aldose is a pure sugar. | Ketose is an impure sugar. |
| Chemical Formula | The chemical formula of Aldoses is written as Cn(H2O)n. | The chemical formula of ketose is written as RCOR. Where R is the ketose functional group (-C=O). |